Rand Recovery
15 June 2020 By PDSNETThe rand is arguably one of the most volatile and difficult currencies to predict. It is very liquid and is the preferred emerging market currency of international currency speculators. It has become a ping-pong ball which reflects the spasmodic shifts between “risk-on” and “risk-off” sentiment on the world stage.
If international investors get scared, then the rand falls – and quickly – as they withdraw their funds from here and buy long-dated US treasury bills. And then it rallies gradually as panic fades and awareness grows of our low inflation rate, relatively stable and high real interest rates.
Last Thursday (11-6-20) Wall Street had a momentary panic attack which drove the S&P down 5,9% in a single day. This panic was caused by a sudden renewed fear of a “second wave” of the coronavirus pandemic and concerns that the recovery in the US would not be as rapid as previously hoped.
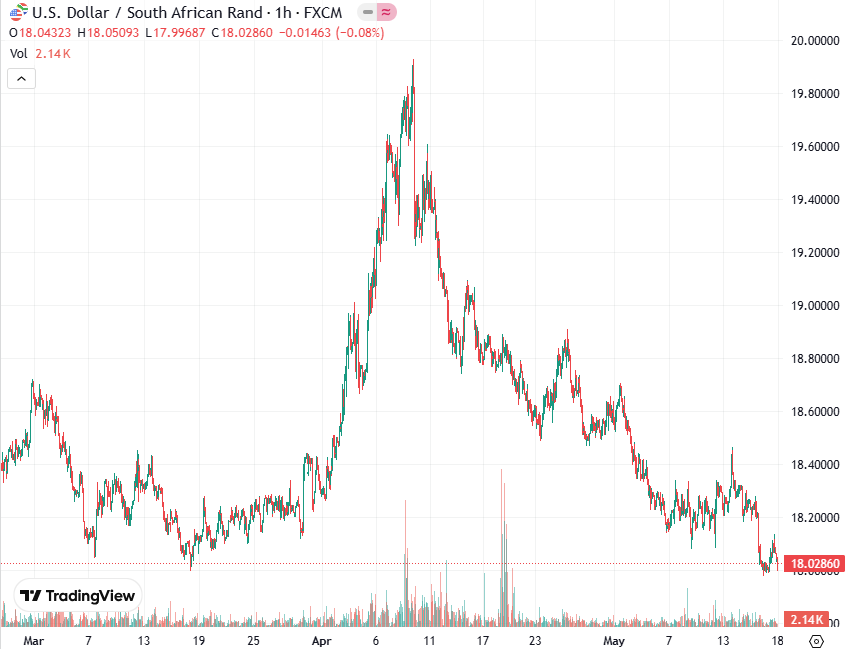
The rand, which had been strengthening steadily to that point, responded by immediately collapsing from around R16.43 to the US dollar to R17.30. It lost over 5% in just two hours. Then, as the panic in the US subsided, it stabilised and began to claw its way back. Consider the chart:
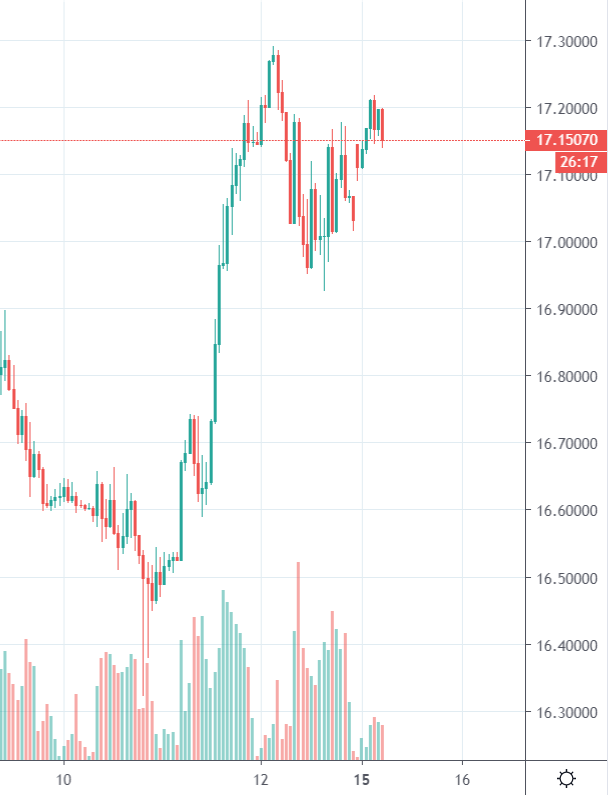
(Chart by Dynamic Outcomes: https://www.forexforecasts.co.za/resources/live-charts/)
That panic may not yet be over and there may be further downside both in the S&P and the rand, but it shows clearly how the rand is a sensitive and volatile barometer of international sentiment.
What seems undeniable to us, however, is that the rand is fundamentally under-valued on world markets and that it is steadily strengthening over the longer term. While there can be little doubt that the economy’s situation is parlous from a local perspective, everything is relative and overseas investors tend to see us as a better investment opportunity than other emerging economies such as Brazil, Turkey or Russia. Consider the chart:
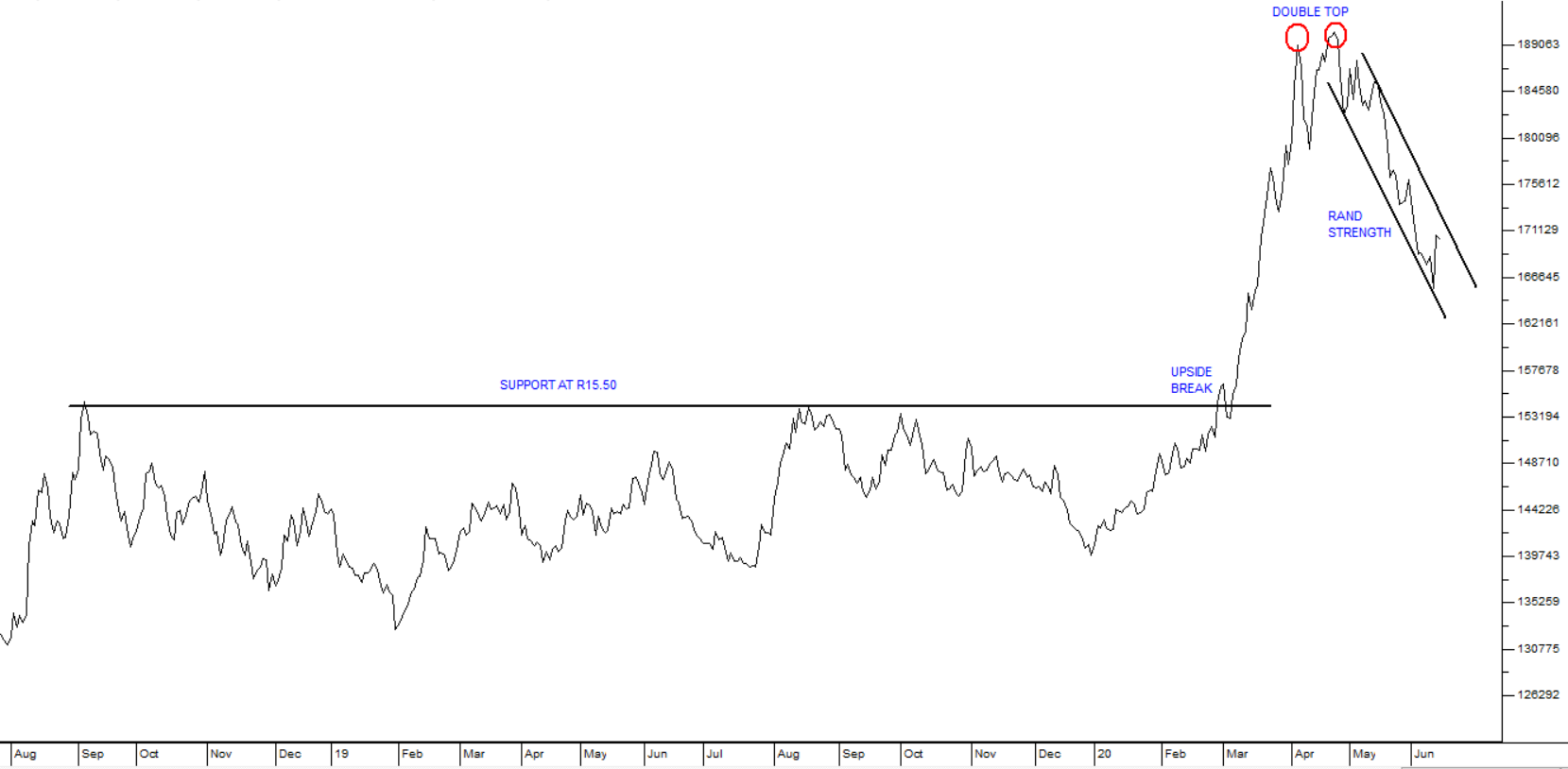
Here you can see the upside breakout above the R15.50 support level in late February 2020 and the sharp impact on the rand as international sentiment, faced with COVID19, moved rapidly to “risk-off”. This was followed by a “double top” in April 2020 and then a fairly quick recovery – which is still on-going.
We see the rand as exposed to periodic waves of “risk-off” sentiment, but as continuing to strengthen over the medium term. This perception should inform your decisions on rand hedge shares as you look forward to next year and the inevitable recovery of the world economy. The simple fact is that international investors will always be flighty – but they always are drawn to real rates of return on our long bonds and so, as soon as any panic is over, they return here in their droves.
DISCLAIMER
All information and data contained within the PDSnet Articles is for informational purposes only. PDSnet makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, suitability, or validity, of any information, and shall not be liable for any errors, omissions, or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. Information in the PDSnet Articles are based on the author’s opinion and experience and should not be considered professional financial investment advice. The ideas and strategies should never be used without first assessing your own personal and financial situation, or without consulting a financial professional. Thoughts and opinions will also change from time to time as more information is accumulated. PDSnet reserves the right to delete any comment or opinion for any reason.
Share this article: