Oil
21 September 2020 By PDSNETThe Oil market is usually an excellent barometer of the state of the world economy. When there is growth, people buy more cars and drive more, more products are consumed which means they have to be transported to retail outlets – usually by an internal combustion engine of some sort.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused the oil price (North Sea Brent) to collapse to prices below $20 a barrel as lockdowns around the world cut vehicle usage sharply. As the worldwide wave of lockdowns subsides, the demand for oil has been picking up. In fact, at the end of August 2020, North Sea Brent was back trading above $45.
Then the price suddenly collapsed back to below $40, just as the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) was hosting its annual meeting in Baghdad – online this time. It appears that demand for oil has been lower than was expected. In the United States, the driving season (summer) is now almost over and fuel sales are still down about 20% from last year. In China and India, who are both significant users of oil, demand is also down by about a fifth.
It is apparent that following the pandemic, businesses and individuals have found ways to travel less. Business meetings are being held remotely online and thousands of consumers are now working from home in a trend which is unlikely to be reversed. At the same time, the move to electric cars and trucks is slowly gaining momentum. It is just possible that the drop in oil demand is reflecting a new post-COVID-19 normal.
Of course, OPEC is plagued by a group of its members who persist in reneging on their agreements and supplying more oil to the market than they should. There is also the possibility that Saudi Arabia and other major members of OPEC will arrange for further cuts in production to push the price up. OPEC has now been around for 60 years, but trying to manage a cartel of highly disparate members in the face of weak oil prices is becoming increasingly like trying to herd cats.
Many of the smaller producers in the cartel, like Nigeria and Venezuela, simply cannot survive at $40 per barrel, but they are also usually the ones selling oil above their OPEC quotas. Even the United Arab Emirates (UAE), a staunch member of OPEC, has admitted to selling 20% more than its quota. OPEC recently reduced the flow of oil from 9,7 million barrels per day to 7,7 million, but the actual supply is somewhat more than that and this fall in the price has come despite that restriction.
Of course, it is always well to remember that at prices between $40 and $50, shale gas production becomes viable – which tends to place a cap on how high the oil price can go. Rising shale gas production probably accounts for the slowdown in the pace at which the oil price was climbing for the 3 months from the beginning of June to the end of August. Consider the chart:
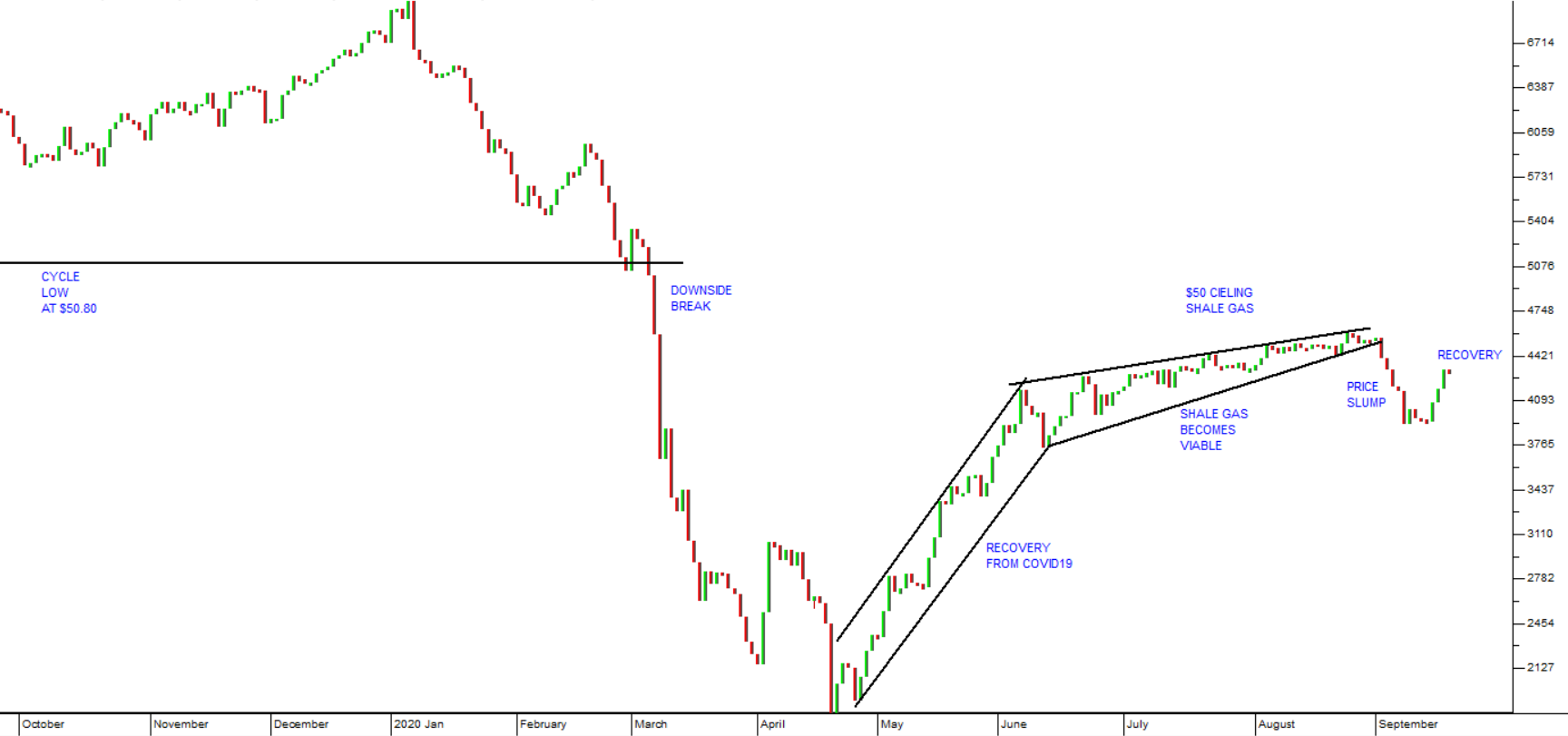
Here you can see the support level at $50.80 per barrel from the previous cycle low - and the downside break which we drew your attention to in our March 2020 Confidential Report. COVID-19 took oil down to a low just below $20 and then it recovered steeply in the second half of April and May 2020. Once the price rose above $40, more and more shale gas producers began to produce again, slowing oil’s advance.
That advance was brought to an abrupt end by a two-week price slump starting on 2nd September 2020. Apparently, oil stores were over-full and off-take was limited by the end of the US driving season. In the last three days oil has recovered somewhat, but is still below the $45.93 high that it made on 25th August 2020.
It is also well to consider the correction taking place on Wall Street at the moment. That has seen the S&P500 fall about 7,3% from its record high of 2580 also made on 2nd September 2020. We know that there are a few oil stocks in the S&P500, but not enough really to account for this downward move.
Nothing in the markets moves in a straight line. There will always be corrections. But we are satisfied that the great bull trend which began in March 2009 is still in progress. So, our view is that this correction should probably be regarded as a buying opportunity.
DISCLAIMER
All information and data contained within the PDSnet Articles is for informational purposes only. PDSnet makes no representations as to the accuracy, completeness, suitability, or validity, of any information, and shall not be liable for any errors, omissions, or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. Information in the PDSnet Articles are based on the author’s opinion and experience and should not be considered professional financial investment advice. The ideas and strategies should never be used without first assessing your own personal and financial situation, or without consulting a financial professional. Thoughts and opinions will also change from time to time as more information is accumulated. PDSnet reserves the right to delete any comment or opinion for any reason.
Share this article: